In this post I will cover the basics of HBase Architecture. How data is stored in HBase and what are components that are available in HBase.
HBase Architecture: Data Model
HBase looks like a relational Data Base as it contains row and columns, but it is not a relational database. Relational databases are row-oriented whereas HBase is NoSQL column oriented DataBase.
Row-oriented database stores the data in the sequence of the rows whereas Column-oriented database stores the data in the sequence of the columns.
To understand the Data Model of the HBase, let us consider a Customer Product Table

RDBMS will store the data in rows i.e. 1st-row data followed by 2nd-row and so on and the data looks like
101, A, India, 201, Milk
102, B, LA, 202, Schezwan Rice
103, C, US, 203, Butter
In columnar database, column values are stored together. Like all the values of the 1st column will be stored together followed by all the values of the 2nd column and in the similar way values for the other columns will be stored.
101, 102, 103, A, B, C, India, LA, US, Milk, Schezwan Rice, Butter
HBase Architecture: HBase Table Structure
HBase table comprises of Row Key, Column Family, Column Qualifier and cell. Consider the above table to understand the concept of HBase table structure.
We have 5 columns in the table, where:-
- CustomerID is unique and can be considered as Row Key.
- Name and Location represents Customer details, can be mapped to Customer Family.
- ProductID and ProductName represents the Product Details, can be mapped to Product Family.
- Column names are considered as Column Qualifiers.
Visual representation of the HBase table looks like
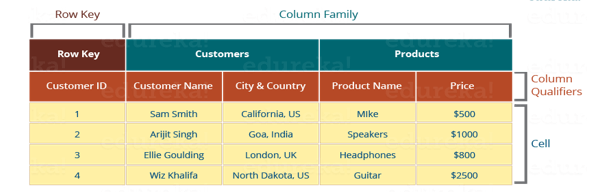
Image Courtsey:- Edureka
Row Key: – Row keys are the unique values present in the table. These can be considered the same as Primary Keys in RDBMS. These are used to make the search process fast.
Column Family: – Combination of the various columns are known as column family, a family are combined on the basis of the similarities between them, like columns containing all the details of the customer can be mapped to the customer column family. Data for the same column family are accessed together and hence it makes the search process faster.
Column Qualifiers: – Column names in HBase are known as column Qualifiers.
Cell: – Data is dumped into the cells which are identified by row keys and column qualifiers.
HBase Architecture: Components
HBase consists of the different components, which are helpful in the HBase processing. Like Hadoop, it has name node, data node, zoo keeper. Mostly HBase consists of HMaster and 3 or more region servers. To provide HA, backup master runs on the other hosts than the active master host. HBase consists of below components:-
- HBase Master
- HBase Region
- HBase Region Server
- Zookeepe
HBase Architecture: HMaster

Hbase coordinates the HBase cluster and is responsible for managing all the activities performed on HBase, including region servers and metadata changes. In distributed clusters, Master runs on the name node. HMasters functionality can be considered the same as that of the Hadoop name node which manages the data nodes. We can keep a single HMaster if we are deploying HBase on a standalone cluster and set have an active and a backup HMaster if we are deploying on the distributed cluster.
- Perform all the DDL operations.
- When HBase starts up HMaster assigns the regions to the region server and re-assign in case of recovery and load balancing.
- It keep tracks of the activity and states of the region server with the help of zookeeper and when any region server goes down it performs recovery activities.
- It provides the interface for performing DDL operations such as create, update and delete the table.
- Backup HMaster became the active when the active goes down. Active HMaster sends the heartbeat to the zookeeper and Inactive HMaster keeps listening to the heartbeat and become active when Active HMaster goes down.
HBase Architecture: Region Server
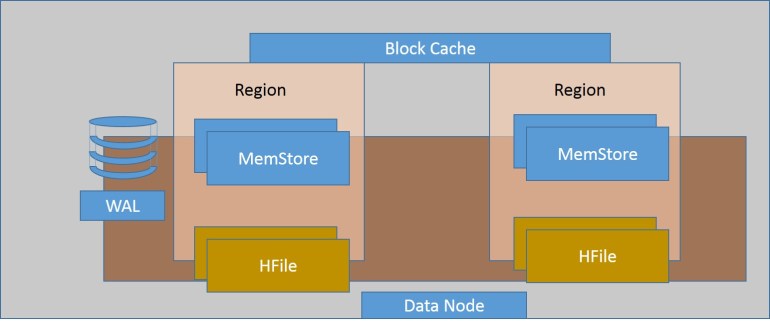
A region server is considered as a worker node which handles all the read, write, update, delete requests from the clients. There are multiple region servers available in HBase. Region server runs on top of the HDFS and region server process runs on every node of the cluster. Below are the components of the region server:-
Block Cache:- Block Cache resides on the top the Region Server. These are in general can be called as in-memory. It holds the recently read data, when we query on the recently read data, computation is performed on the block cache data to provide faster read result. Whenever block cache gets full the least recent data gets removed.
WAL:- WAL stands for Wall Ahead Logs. This is a file attached to the Region Server inside distributed environment. WAL can be considered as a file which keeps all the record and logs of the operations performed on HBase. It consists of the newly added data that has not been persisted or committed to the permanent storage i.e. HDFS or S3 or any storage area. In general, whenever an operation is performed on HBase it goes to the WAL first. WAL is used to recover the data set in case of any failure occur.
MemStore:- MemStore is considered as a write Cache. Whenever data is added to the HBase, it first goes to the MemStore and MemStore commits the data to the disk or permanent memory. There is one MemStore for each column family in a region. There are multiple MemStores in a Region because a Region contains multiple column families. Data in the Memstore is stored in the lexicographical order before storing it to the disk.
To understand the concept of MemStore in an easy manner, consider the above table where we have 2 column families’ customer and product. Data of the customer column family will go to one MemStore file and of product to another MemStore file. The default size of the MemStore file is 256MB which can be configured by using property hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size. Data from the MemStore can be flushed to the HDFS depending upon the two factors. One, when the MemStore size reaches the limit set by the hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size property. Second, whenever the heap size of the threshold reach the limit specified by the property hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit. When the threshold property is reached all the MemStore gets flushed. Why, This force flush is needed, consider a scenario, there are multiple MemStore and their size is not reaching to the memstore flush size value, so no data will be flushed and the large number of the open MemStore will be available causing to reach the threshold, which might cause issue to the region server. To avoid this situation MemStore needs to be flushed when they reach to a threshold value.
MemStore store the Data in an orderly manner before sending it to the permanent disk. This help in achieving the best performance for the read operation in HBase. We will read more on this in the upcoming blog.
- HFile: – HFile is the actual storage file that stores the rows as sorted key values on a disk. When the size of the MemStore gets exceeds, it stores the data to the HDFS in the HFile.
Data in the HFile is in sorted format. Whenever any read operation is performed data is read from the HFile which is in sorted order as per the row key value which helps in faster read operation.
What happens if small row value is inserted after writing the data to HFile?
Consider an example we have set up the value of the hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size to ‘256 MB’. We have considered row key as a sequence value. While inserting the 1st set of the data I have values from 1 to 300 but we do not have any values for sequence 10, 18, 100. Say after writing from 1 to 256 sequence, MemStore size got exceed and it writes the data to the HFile File1, and remaining data is in MemStore in the order from 257 to 300.
File1 will look alike
1,2,3,….,9,11,….,17,19,…….99,101,……..256
MemStore will look alike
257,258………………………………………….300
If data is inserted for the row keys 10, 18 in the later stage, how the data will reside. As per the HBase terminology, data will reside in a sorted order. In that case sequence 10, 18 must be written to File1. As File1 is already flushed to the HFile, no operation will be performed on that file. The new data will be written to the MemStore and 10, 18 key sequences will be in beginning and the MemStore will become
10,18,257,…………………………………………….300
HBase Architecture: Region
Regions reside inside the region server. There are multiple regions inside a region server. A region consists of all the rows between the start and end key assigned to that region. HBase table can be divided into the region in such a way that all the columns of a column family reside in a particular region.
The default size of the region is 256MB which is configurable.
HBase Architecture: Meta Table

We have learned about the HBase architecture, region servers, and regions. The question might arise from where HBase will get the list of all the Region Server. To your answer, Hbase META TABLES were previously called as META tables store the list of all the Region Servers available in HBase. Location of .META table is stored zookeeper and its name become hbase:meta
.META maintain the tables in key-value pairs. Key represents the start key of the region and its id whereas the value contains the path of the Region Server.

