Data Lineage
Data lineage can be defined as the life cycle and end to end flow the data. This lifecycle includes the origin of the data, how it moves from one point to another and where the data currently resides. Using the data lineage organizations can get a better understanding of what is happening with the data, as it flows through different pipelines (DataLake, ETL, reports etc.), and provides more visibility for the analysis purpose, which can play the vital role in making important business decisions. In general, data lineage shows the pictorial representation of the flow of the data from the origin to the destination.
Data lineage enables the companies to trace sources of specific business data, which enables them to track errors, implementing the changes in process, and implement the system migration to save the significant amount of the time.
Data Governance
Overall management of the data is mainly known as Data Governance. Data is managed is required to ensure the availability, quality, integrity, and security of the data throughout its lifetime. Data governance includes ensuring the process required for establishing the process required to manage the quality of the data, accountability for the poor data quality and ensure the enterprise data can be used throughout the organization.
Data Lineage in Hadoop
Data lineage in Hadoop can be considered as from where the data is coming to the cluster and how data is being used in the cluster. Hadoop tools (Apache Atlas for Hortonworks and Cloudera Navigator for Cloudera) can be used as a visualization tool for tracking data and its transformations from upstream to downstream through the cluster. Lineage can show the transformation produced to the data coming from the source system on the column level.
Lineage using Hadoop Distribution
Apache Atlas, mainly track the data lineage for
- HDFS File Process
- Hive tables and columns
- Hive queries
- Sqoop data flow
- HBase tables
Cloudera Navigator, mainly track the data lineage for
- HDFS File Process
- Datasets, and directories
- Hive tables and columns
- Hive and Impala queries
- MapReduce and YARN jobs
- Pig scripts
- Oozie workflows
- Spark jobs
- Sqoop jobs
Sample Example using Apache Atlas
In this post, I am going to share a few examples using Apache Atlas for the Hive and Sqoop processes.
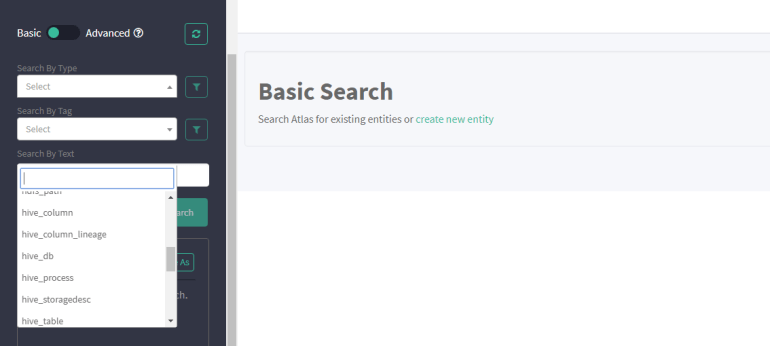
An overview of the Apache Atlas UI:-
The below image represents the Apache Atlas UI. In the drop-down window, there are multiple options to select Hive db, Hive Table, Hive columns, Hive column lineage, Sqoop process, Hdfs, HBase etc. Click on any option as per the requirement.
Data Lineage for Hive Table Insert Operation
Below images represent the Data Lineage flow for the Hive tables. In fig1, data is inserted from one Hive table to another. The table showed in the red is the destination table or the point at which you are tracking the lineage. The process marked in blue shows the operation happening between the source and the destination.

Figure:-fig1
Fig2 shows a complex process as compare to the fig1, where the data is inserted from three Hive tables to the fourth one. The operation popped in the red is the table for which I am checking the lineage.
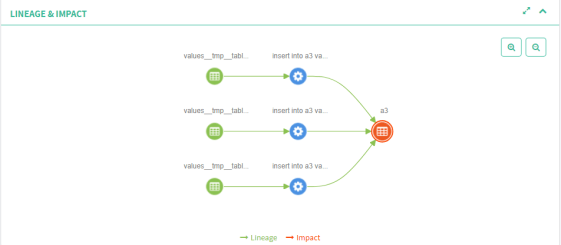
Figure:-fig2
How Apache Atlas Generate Lineage
After having a look at the above images, you might be thinking how Apache Atlas creates a lineage for any process in Hadoop. There is no manual steps needs to perform for generating the Lineage. Apache Atlas listens to the Kafka topics “Atlas Hook” and “Atlas Entity”. There are inbuilt hooks available for the different ecosystems like Hive Hook, Sqoop Hook, HBase Hook, which integrates the ecosystem with Apache Atlas. whenever any table is created in Hive or any operation is performed in the Hive or any import/export operation is performed using Sqoop, all the data is popped using the Kafka topic to the Atlas and with the help of the available Hooks, atlas creates the required lineage for the process.

